Editor and project manager Derek Philip-Xu shares with us the ins and outs of his varied week in the world of English language teaching (ELT) editing, where he focuses on producing digital content for publishers.
My route into publishing
I’ve been involved in ELT and publishing for over 20 years now, but I initially started off my work life as a chartered surveyor. That was a career path I followed for seven years before deciding to take a career break. I wasn’t keen on backpacking, but my sister’s suggestion of teaching English abroad sparked my interest. While she was thinking that it would be good for me to travel the world and gain valuable work experience, she was also hoping to visit me for nice holidays somewhere in Europe.
In 2003, following completion of my CELTA (Certificate in English Language to Speakers of Other Languages), I moved to Japan to teach for a year. This was not because I didn’t want family visits, but there was something about Japanese culture and the way of life that I found quite captivating. A year out turned into five years, followed by two years teaching in Spain and then six years in China. My time in China saw me move from teaching into publishing, developing both print and digital materials for young learners. When I returned to the UK, I continued working in publishing, specifically on digital ELT materials.
Why the focus on digital content?
I have always believed that digital products are an important part of a publisher’s course offering. They are not just a free add-on, as I have sometimes heard them described. They take time and effort to produce and, as was seen throughout the pandemic, offer teachers and students the opportunity to continue their classroom activities – albeit in a slightly different format than before. Digital ELT content continues to offer flexibility in the form of micro-learning and bite-sized learning. Students can practise their English wherever they are and whenever they want, providing them with a degree of control and choice that wasn’t available when I started out.
So, what is a typical week?
Well, is there such a thing as a typical week? Probably not, which is quite nice as it keeps things fresh and interesting. Generally, I start off the week with an overview of the tasks I need to get through. I use a handy business and project management app called Notion to organise my workload into projects, to-do lists and due dates. It quickly gets me into the work mindset, setting me up for the week ahead.
If I’m lucky enough to come into a project right from the very beginning, there will be a project kick-off meeting scheduled at some point. For example, one of my clients has asked me to join the project team as a content editor for a digital component the client is developing. I’ll be making sure the content that is written follows the brief, is pedagogically sound and is generally fit for purpose.
Project kick-off meetings, whether I’m the project lead or part of the project team, are an excellent way of ensuring that everyone is on the same page. Sometimes aspects of the project have not yet been decided on, such as the overall platform design, and these meetings are a good way of communicating those known issues but also assuaging any uncertainties that team members might have. They are a good opportunity to start building rapport with the rest of the team, ask any questions, present any doubts and generally get up to speed with the project and its documentation.
Project update meetings follow on from the kick-off meeting and can range from quick 15-minute weekly catch-ups to longer meetings once or twice a month. Project management is a lot about communication but also involves information gathering, and project update meetings are a useful tool for that. It is vital that the correct people have the most up-to-date information so that the project can proceed smoothly. In my project update meetings, we are looking at changes to the schedule to bring forward the go-live date, as well as interrogating the existing publishing workflow to ensure that it fits with the schedule and the budget.
My publishing work as a digital commissioning editor has set me up well for dealing with project management tasks, and, indeed, there are many crossovers (such as scheduling, briefing and budgeting). I am currently building on that knowledge through studying with the Association for Project Management. Nevertheless, having worked with publishing workflows for many years, and understanding the bottlenecks and pinch points that invariably crop up, it has become easier to anticipate and, therefore, deal with such issues.
Editing work
One of my regular jobs is working as editor of Voices, the flagship magazine of the International Association of Teachers of English as a Foreign Language (IATEFL). This is a mix of editorial and project management work. For project management, this involves setting schedules and ensuring that authors and contributors submit their articles by the specified deadlines and generally progress everything through the workflow in a timely manner.
The editorial part of the work involves me liaising with the authors, providing advice and feedback on their work. This is a very satisfying part of the job as I get to speak regularly with IATEFL members from all over the world, helping them with their articles on a wide range of ELT-related subjects. Many of the authors are writing in their second language, which is no easy feat. I aim to guide them through the publishing process by first asking them to submit a short outline of their article which I can provide feedback on. This provides the author with a foundation upon which to start writing their article in more depth. There can be regular check-in points just to make sure that good progress is being made and to resolve any potential issues. Once submitted, I give the article an initial edit before sending it off to the copyeditor.
This culminates in the proofing stages, where I get to work closely with the designer and the copyeditor, checking to ensure that everything is in the correct place. One important aspect of our work is our desire to make the publication more accessible. This has involved checking the fonts and font sizes used throughout and updating to sans serif fonts, to improve readability. We are also looking at including alternative (alt) text descriptions for images which can be read by screen readers.
Running my business
I do not particularly like the term ‘freelancer’ because it sounds so temporary; I am a self-employed business owner. Although the projects I take on may last a few months or maybe only a few weeks, there is nothing temporary about the business I am running. While I have to work on my project tasks, such as the content editing and project management (the money makers), I do also have to spend time during the week on business admin and other similar tasks.
Jobs will not come in if people do not know you or what you do. So, there has to be some element of networking to increase my business visibility and online presence. Although I’ve gotten better at networking over the years, it’s not something I particularly like doing. Nevertheless, going to the IATEFL conference as well as the ELT Publishing Professionals Freelancers’ Awayday is invaluable (and fun).
Concentrating on the likes of your accounts from a business health standpoint as well as increasing your visibility as a business has an impact on your project pipeline. It is important to ensure that you plan ahead and know how much time you have available throughout the coming months and, potentially, for the year ahead. Some projects will tide you over for a few months, with others being more short term. With increased visibility, you may often be contacted at short notice to see if you are available to take on work. I have my time-tracking spreadsheet at the ready to see exactly how much time I have available and when.
Running
My week wouldn’t be complete without a few runs around Maidenhead, where I live. I’ve been involved with Maidenhead Athletic Club for around six years now, most recently as the club’s chair. Getting out and about for a run, no matter how fast or slow, is a great way to wind down after a busy day. Running is great for alleviating stress and anxiety, and for rooting you in the present. I’d definitely recommend it after a busy day of project management and editing.
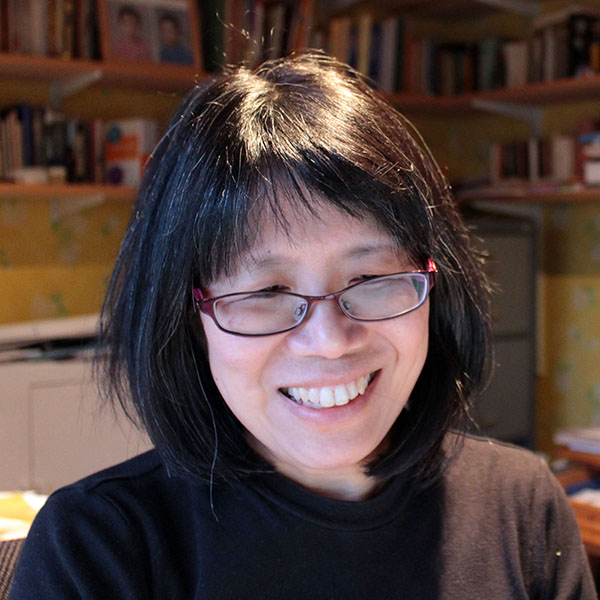
About Derek Philip-Xu
Derek Philip-Xu left his native Scotland in 2003 to teach English in Japan and Spain before moving into school management and publishing while in China. On moving back to the UK in 2016, he continued working in ELT publishing, specialising in digital content development and commissioning. Derek is now self-employed, managing his business Refreshing Publishing, which offers digital content development, publishing project management and editorial services.
 About the CIEP
About the CIEP
The Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP) is a non-profit body promoting excellence in English language editing. We set and demonstrate editorial standards, and we are a community, training hub and support network for editorial professionals – the people who work to make text accurate, clear and fit for purpose.
Find out more about:
Photo credits: desktop by Pexels on Pixabay; team meeting by fauxels on Pexels.
Posted by Sue McLoughlin, blog assistant.
The views expressed here do not necessarily reflect those of the CIEP.